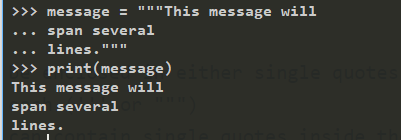
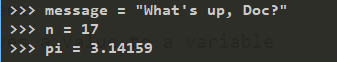
ASCII is a simple form of Unicode text, but just one of many possible encodings and alphabets. Text from non-English-speaking sources may use very different letters, and may be encoded very differently when stored in files.
ASCII
ASCII, abbreviated from American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Most modern character-encoding schemes are based on ASCII, although they support many additional characters.
...