Monolithic Architecture
To start explaining the microservice style it’s useful to compare it to the monolithic style: a monolithic application built as a single unit. Enterprise Applications are often built in three main parts: a client-side user interface (consisting of HTML pages and javascript running in a browser on the user’s machine) a database (consisting of many tables inserted into a common, and usually relational, database management system), and a server-side application. The server-side application will handle HTTP requests, execute domain logic, retrieve and update data from the database, and select and populate HTML views to be sent to the browser. This server-side application is a monolith - a single logical executable. Any changes to the system involve building and deploying a new version of the server-side application.
Such a monolithic server is a natural way to approach building such a system. All your logic for handling a request runs in a single process, allowing you to use the basic features of your language to divide up the application into classes, functions, and namespaces. With some care, you can run and test the application on a developer’s laptop, and use a deployment pipeline to ensure that changes are properly tested and deployed into production. You can horizontally scale the monolith by running many instances behind a load-balancer.
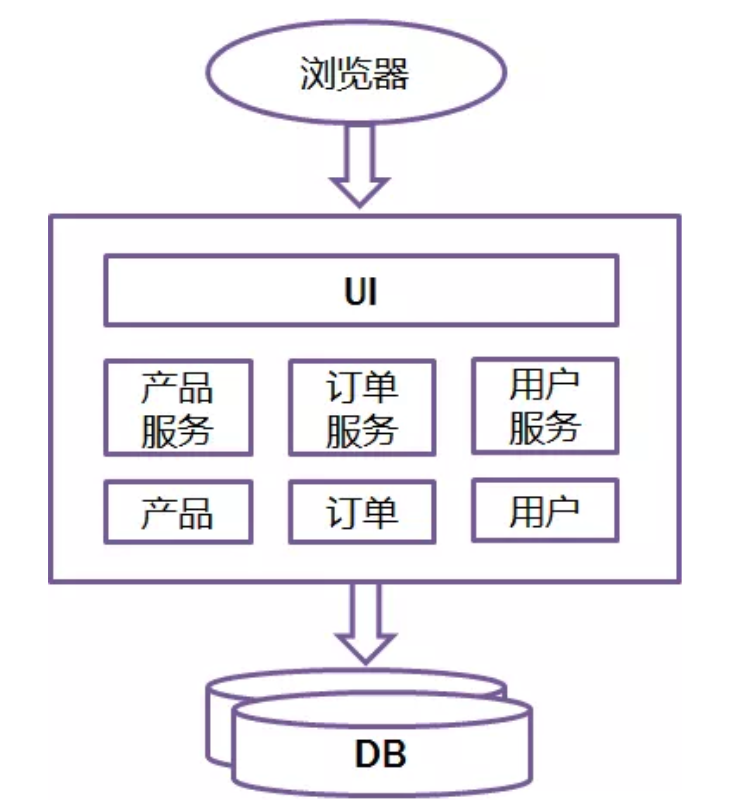
以Java为例,所有的功能打包在一个 WAR包里,基本没有外部依赖(除了容器),部署在一个JEE容器(Tomcat,JBoss,WebLogic)里,包含了 DO/DAO,Service,UI等所有逻辑。
...