What Is Database Sharding?
Sharding is a method for distributing a single dataset across multiple databases, which can then be stored on multiple machines. This allows for larger datasets to be split in smaller chunks and stored in multiple data nodes, increasing the total storage capacity of the system.
Sharding is known as partitioning, and each smaller subsets called prtitions
Similarly, by distributing the data across multiple machines, a sharded database can handle more requests than a single machine can.
Sharding is a form of scaling known as horizontal scaling or scale-out, as additional nodes are brought on to share the load. Horizontal scaling allows for near-limitless scalability to handle big data and intense workloads. In contrast, vertical scaling refers to increasing the power of a single machine or single server through a more powerful CPU, increased RAM, or increased storage capacity.
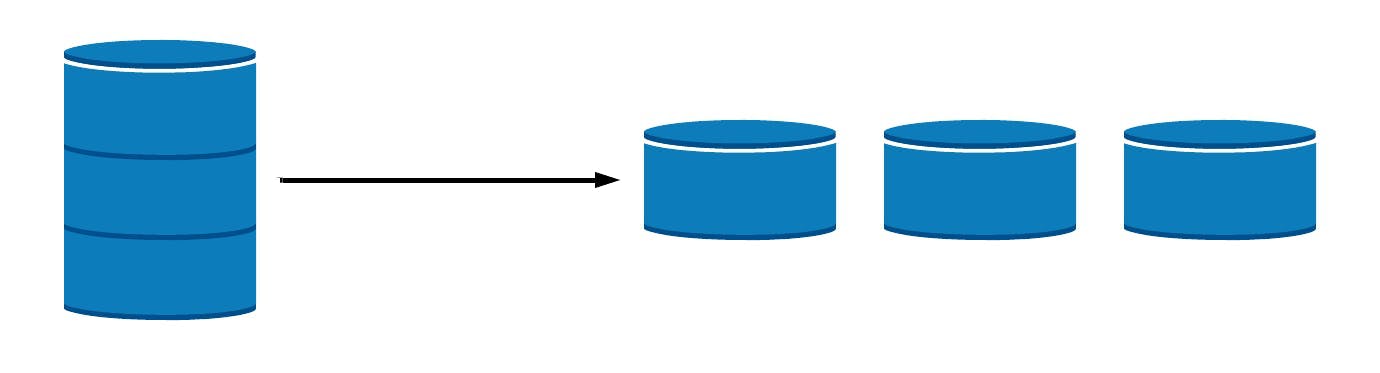
什么时候会考虑分库分表
单库/表太大
- 单个数据库的能力已经达到瓶颈或者存在潜在瓶颈,比如
- Table row count > 10,000,000.
- Table size > 10GB.
- Performance bottleneck (e.g. Querying Response Time < 99%, i.e., more than 1% queries take more than 10ms).
- 单库太大,以至于所在服务器上磁盘空间不足
- 单库上操作出现了I/O瓶颈
解决方法:切分成更多更小的库或者表
水平分库分表(Horizontal Partitioning)
水平分库
当数据库中单表的数据量很大时,采用水平分区的方式对数据进行拆分(将同一个表中不同的数据拆分到不同数据库或同一个数据库的不同表中)。比如,以对某个主键进行hash取模的方式(以保证对N个数据库的访问负载是均衡的),将数据分布表到N个数据库或表中。
值得一提的是,进行分库分表后,进行对跨库的表join、事务操作或者数据统计、排序时,又出现了新的性能问题。
使用原因
大部分互联网业务数据量很大,单库容量容易成为瓶颈,如果希望:
此时可以使用水平切分架构。
一句话总结,水平切分主要解决“数据库数据量大”问题,在数据库容量扛不住的时候,通常水平分库。
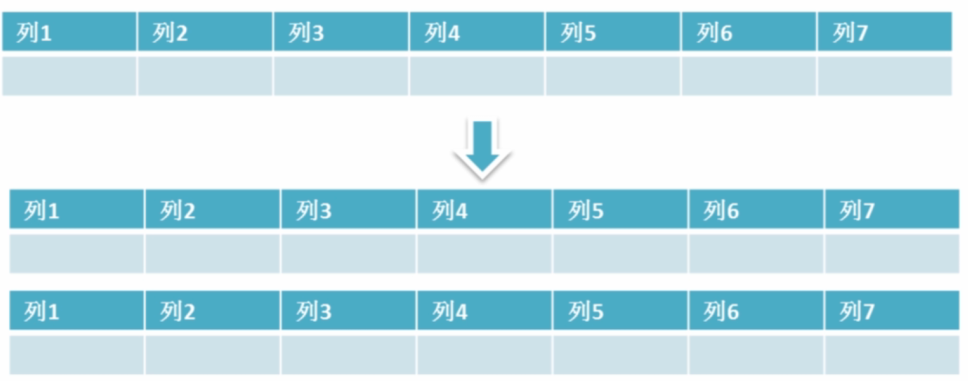
水平分表
水平分表也称为横向分表,比较容易理解,就是将表中不同的数据行按照一定规律分布到不同的表中(这些表保存在同一个数据库中),这样来降低单表数据量。最常见的方式就是通过主键或者时间等字段进行 Hash 和取模后拆分。
...


