JSON Web Token (JWT)
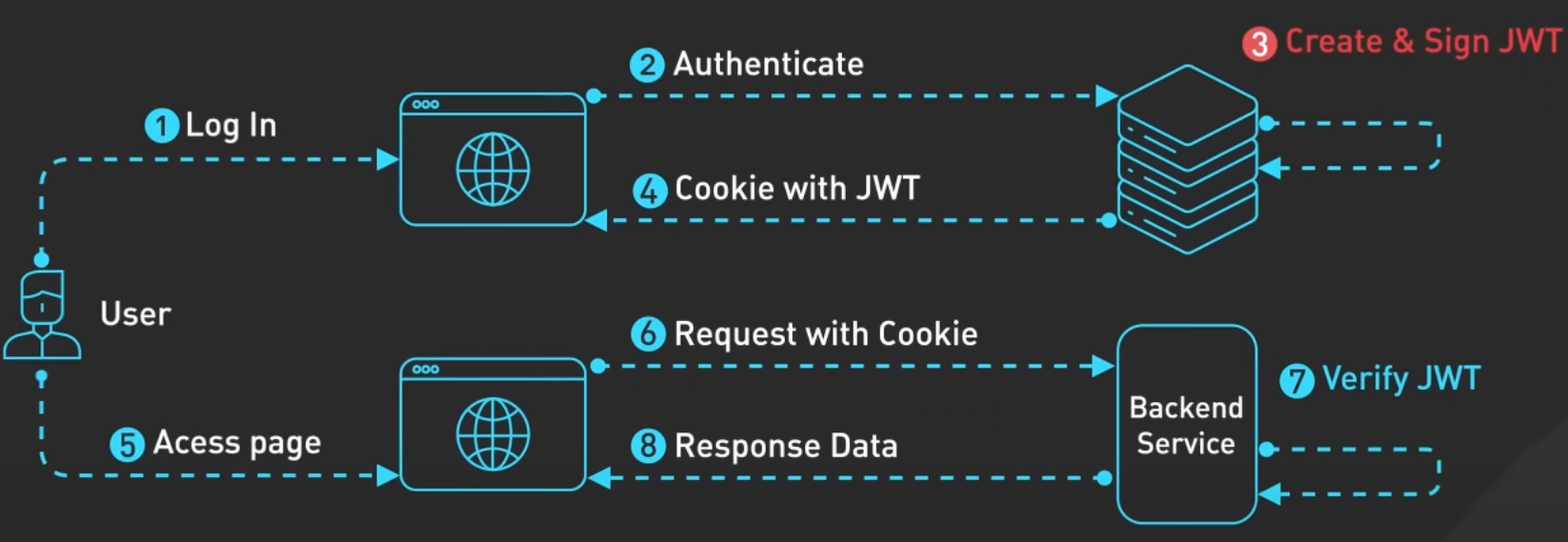
- No separate storage needed
- Invalidation of a JWT is not easy
- Scaling client and server is easy
Structure
The three parts are encoded separately using Base64url Encoding RFC 4648, and concatenated using periods to produce the JWT:
const token = base64urlEncoding(header) + '.' + base64urlEncoding(payload) + '.' + base64urlEncoding(signature)
Header
Identifies which algorithm is used to generate the signature. In the below example, HS256 indicates that this token is signed using HMAC-SHA256. Typical cryptographic algorithms used are HMAC with SHA-256 (HS256) and RSA signature with SHA-256 (RS256). JWA (JSON Web Algorithms) RFC 7518 introduces many more for both authentication and encryption.
{
"alg": "HS256",
"typ": "JWT"
}
Payload
Contains a set of claims. The JWT specification defines seven Registered Claim Names, which are the standard fields commonly included in tokens. Custom claims are usually also included, depending on the purpose of the token. This example has the standard Issued At Time claim (iat) and a custom claim (loggedInAs).
{
"loggedInAs": "admin",
"iat": 1422779638
}
Signature
Securely validates the token. The signature is calculated by encoding the header and payload using Base64url Encoding RFC 4648 and concatenating the two together with a period separator. That string is then run through the cryptographic algorithm specified in the header. This example uses HMAC-SHA256 with a shared secret (public key algorithms are also defined). The Base64url Encoding is similar to base64, but uses different non-alphanumeric characters and omits padding.
HMAC_SHA256(
secret,
base64urlEncoding(header) + '.' +
base64urlEncoding(payload)
)
Symmetric algo: HMAC
Asymmetric algo: RSA/ECDSA