Background
Consistency Model
Sequential Consitency
The sequential consistency model was proposed by Lamport(1979). It is a weaker memory model than strict consistency model. A write to a variable does not have to be seen instantaneously, however, writes to variables by different processors have to be seen in the same order by all processors. As defined by Lamport(1979),[4] sequential consistency is met if “the result of any execution is the same as if the operations of all the processors were executed in some sequential order, and the operations of each individual processor appear in this sequence in the order specified by its program.”
Example
// Thread 1
x = 1
y = 1
// Thread 2
r1 = y
r2 = x
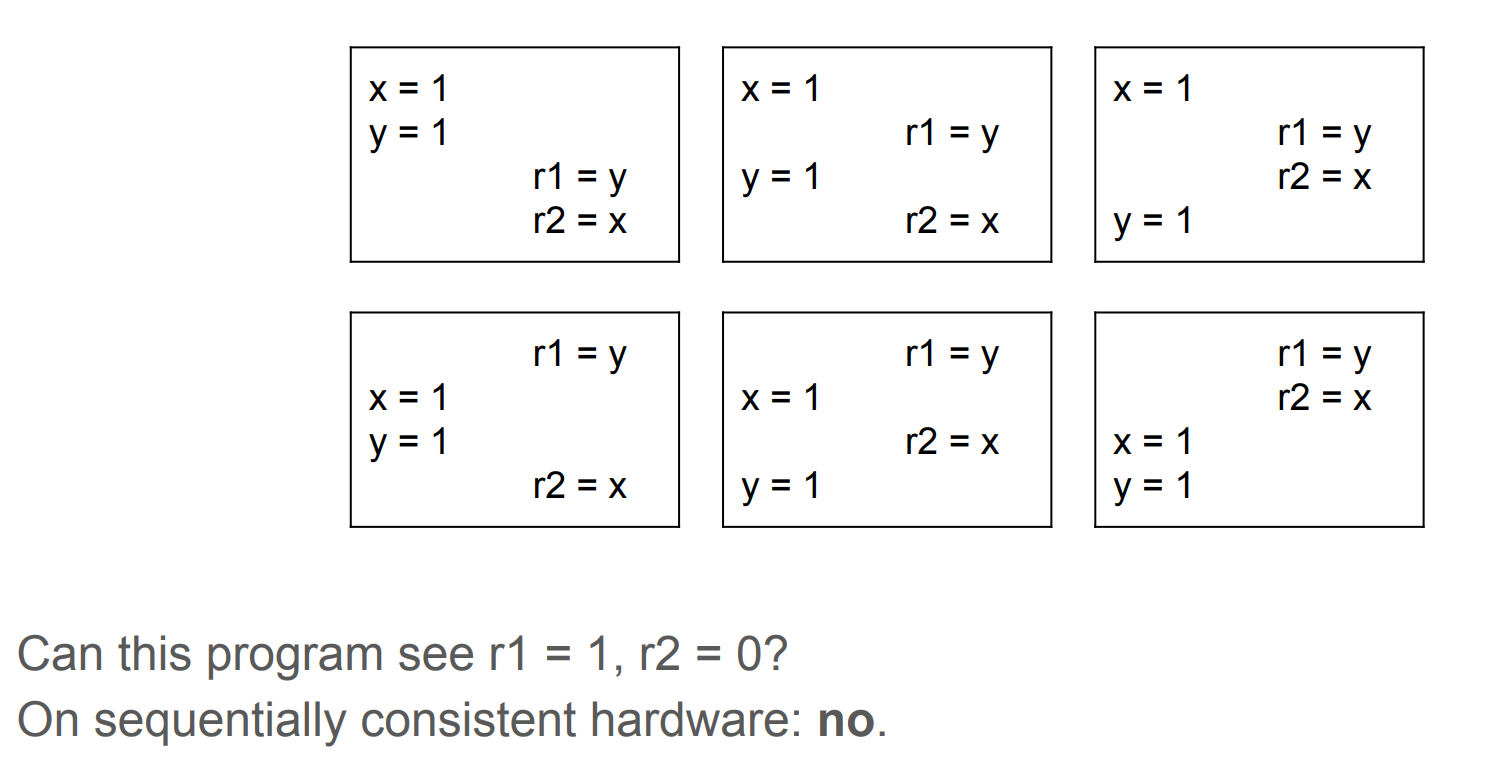
Thread 1’s writes are observed by other threads in original order.
Reference
- https://golang.org/ref/mem
- https://research.swtch.com/mm
- https://medium.com/@edwardpie/understanding-the-memory-model-of-golang-part-2-972fe74372ba
- https://developpaper.com/go-memory-model-in-detail/
- https://go101.org/article/memory-model.html
- http://nil.csail.mit.edu/6.824/2016/notes/gomem.pdf
- https://deepu.tech/memory-management-in-golang/
FEATURED TAGS
algorithm
algorithmproblem
architecturalpattern
architecture
aws
blockchain
c#
cachesystem
codis
compile
concurrentcontrol
database
dataformat
datastructure
debug
design
designpattern
distributedsystem
django
docker
domain
engineering
freebsd
git
golang
grafana
hackintosh
hadoop
hardware
hexo
http
hugo
ios
iot
java
javaee
javascript
kafka
kubernetes
linux
linuxcommand
linuxio
lock
macos
markdown
microservices
mysql
nas
network
networkprogramming
nginx
node.js
npm
oop
openwrt
operatingsystem
padavan
performance
programming
prometheus
protobuf
python
redis
router
security
shell
software testing
spring
sql
systemdesign
truenas
ubuntu
vmware
vpn
windows
wmware
wordpress
xml
zookeeper