PriorityQueue类
PriorityQueue 类在 Java 1.5 中引入。
PriorityQueue 是基于优先堆的一个无界队列,这个优先队列中的元素可以默认自然排序或者通过提供的 Comparator 在队列实例化的时排序。
默认情况下,为最小堆(这意味着,通过 queue.poll() 方法获取的第一个元素为队列中的最小值)。
PriorityQueue 不允许空值,而且不支持 non-comparable(不可比较)的对象,比如用户自定义的类。优先队列要求使用 Java Comparable 和 Comparator 接口给对象排序,并且在排序时会按照优先级处理其中的元素。
PriorityQueue 的大小是不受限制的,但在创建时可以指定初始大小。当我们向优先队列增加元素的时候,队列大小会自动增加。
PriorityQueue 是非线程安全的,所以 Java 提供了 PriorityBlockingQueue(实现 BlockingQueue接口)用于Java 多线程环境。
构造函数
可以在构造函数中指定如何排序。如:
// 使用默认的初始容量创建一个 PriorityQueue,并根据其自然顺序来排序其元素(使用 Comparable)。
PriorityQueue()
// 使用指定的初始容量创建一个 PriorityQueue,并根据其自然顺序来排序其元素(使用 Comparable)。
PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity)
// 使用指定的初始容量创建一个 PriorityQueue,并根据指定的比较器comparator来排序其元素。
PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<? super E> comparator)
自己实现比较器以进行自定义排序
如果希望自己指定比较器进行排序
Queue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(11,
new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer i1, Integer i2) {
return i2 - i1;
}
});
public class PriorityQueueTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
PriorityQueue<People> queue = new PriorityQueue<People>(11,
new Comparator<People>() {
public int compare(People p1, People p2) {
return p2.age - p1.age;
}
});
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
queue.add(new People("张"+ i, (new Random().nextInt(100))));
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(queue.poll().toString());
}
}
}
class People {
String name;
int age;
public People(String name, int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "姓名:"+name + " 年龄:" + age;
}
}
Demo
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue1 = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
queue1.add(2);
queue1.add(1);
queue1.add(3);
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
Integer i = queue1.poll();
System.out.println(i);
}
Comparator<Student> comparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return (o1.id - o2.id);
}
};
Queue<Student> queue2 = new PriorityQueue<Student>(comparator);
queue2.add(new Student(2, "B"));
queue2.add(new Student(1, "A"));
queue2.add(new Student(3, "C"));
while (!queue2.isEmpty()) {
Student s = queue2.poll();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}
public static class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String toString() {
return id + "-" + name;
}
}
}
输出:
1
2
3
1-A
2-B
3-C
实现原理
通过堆实现,具体说是通过完全二叉树(complete binary tree)实现的小顶堆(任意一个非叶子节点的权值,都不大于其左右子节点的权值),也就意味着可以通过数组来作为 PriorityQueue 的底层实现。
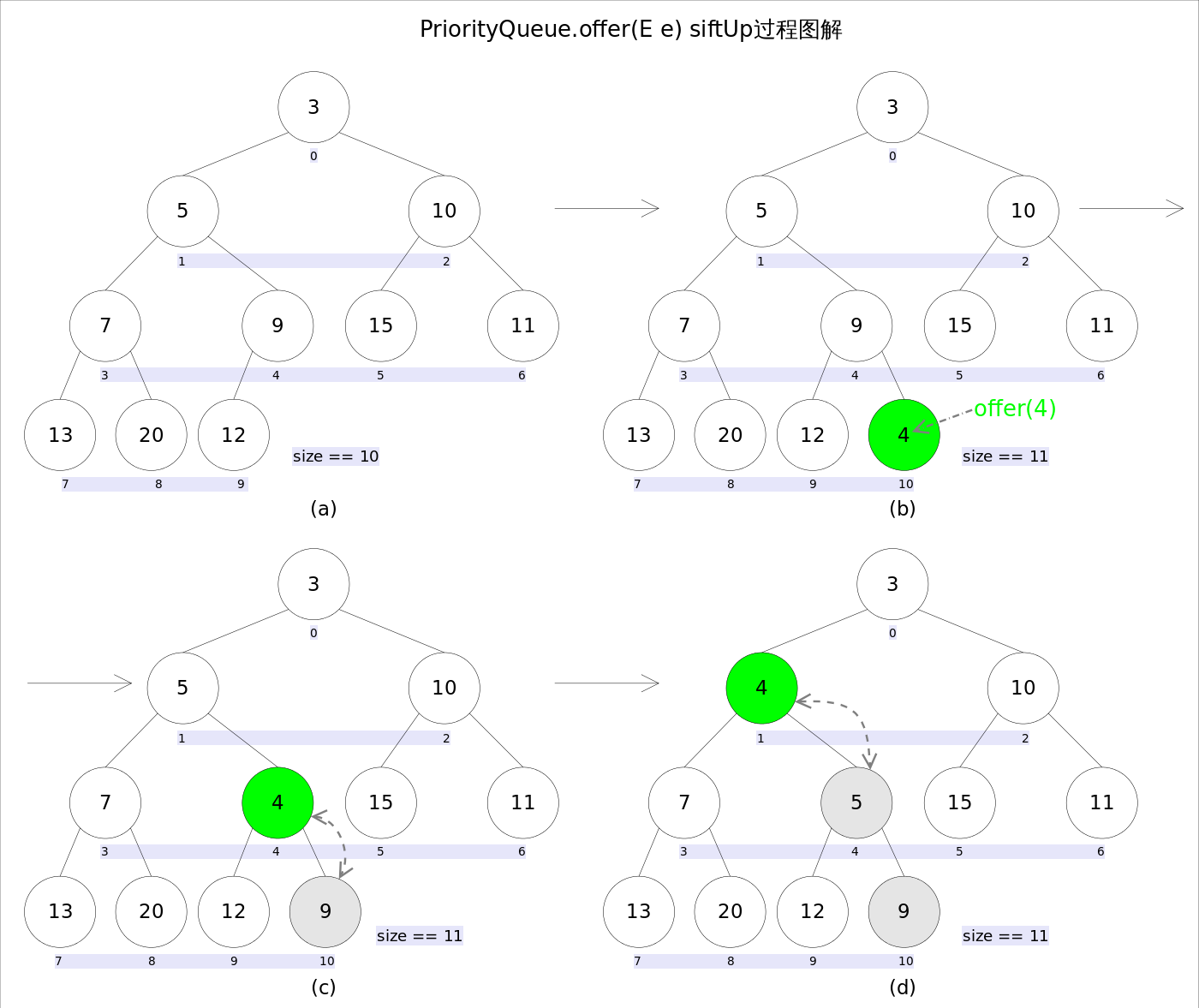
add(E e) / offer(E e) - 添加元素
add(E e) 和 offer(E e) 操作的时间复杂度为 $O(log_2N)$,这两个方法是等同的(equivalent)的,均用于添加一个特定元素到优先队列中:
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
public boolean add(E e) {return offer(e);}
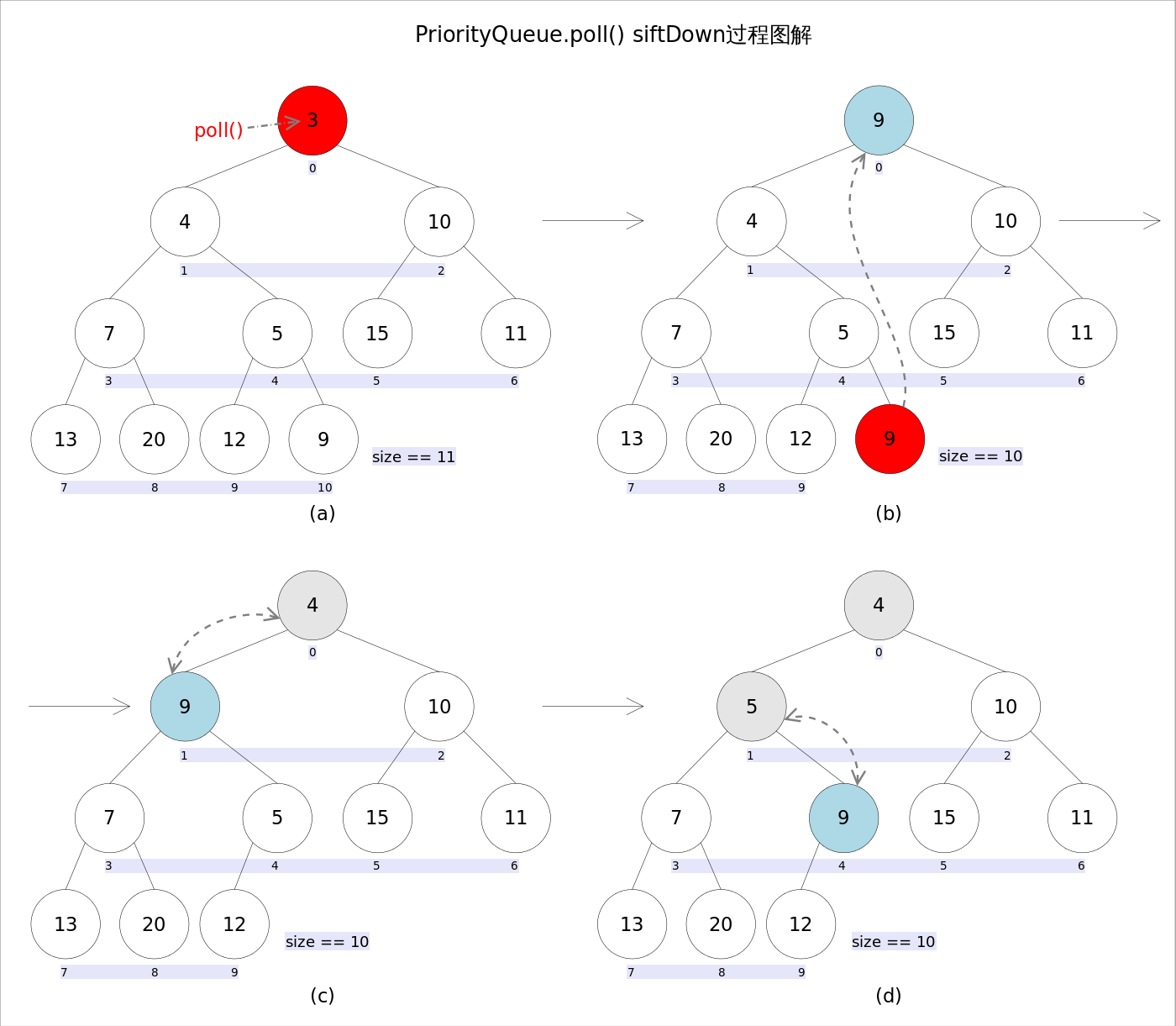
poll() - 移除队头元素
poll() 操作的时间复杂度为 $O(log_2N)$,而 remove(Object o) 方法也用于移除队头元素,但是在调用时,需要传入一个元素,如果这个元素当前处于队头,则移除该元素(并返回 true),否则不进行任何操作(并返回 false)。
public E poll() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
int i = indexOf(o);
if (i == -1)
return false;
else {
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
}
peek() - 获取队头元素
peek() 操作的时间复杂度为 O(1):
public E peek() {
return (size == 0) ? null : (E) queue[0];
}
Reference
- Java学习笔记–PriorityQueue(优先队列)(堆) - https://www.cnblogs.com/gnivor/p/4841191.html
- Java 优先级队列 PriorityQueue - https://www.jianshu.com/p/c577796e537a