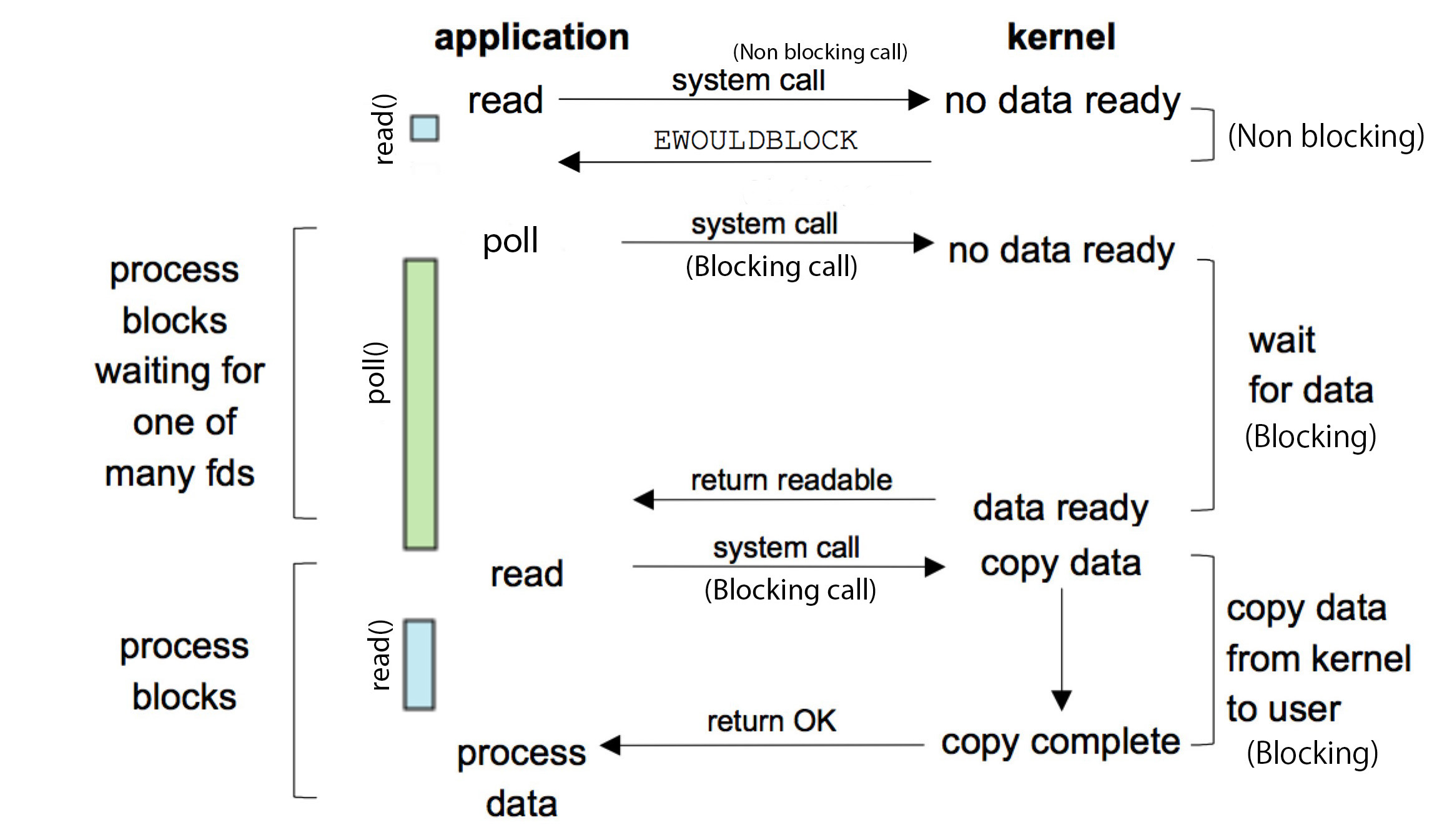
poll
poll在select的基础之上进行改进,并避免不需要的检查。但是,当 fd 较多的时候,它的性能还是十分低下的。通过poll 实现的轮询与select相似,但性能限制有所改善。
#include <poll.h>
int poll (struct pollfd *fds, nfds_t nfds, int timeout);
struct pollfd {
int fd; /* file descriptor */
short events; /* requested events to watch */
short revents; /* returned events witnessed */
};
解释
- 每一个
pollfd结构体对应一个被观察的 fd ; - 在
pollfd结构体中,events字段表示期望被观察的事件(以事件为位掩码表示);revents字段表示被内核观察到的事件,这个字段由内核来设置。因此,所有在events字段中被指定的事件都可能出现在revents中; - 与
select不同的是,在poll中,不需要指定对于异常的监测; poll会返回发生了观察事件的 fd 的数量。当返回0时,说明在达到超时时间后,仍然没有反生任何观察事件;而返回-1说明发生了错误。
一个完整的poll调用例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <poll.h>
#define TIMEOUT 5 /* poll timeout, in seconds */
int main (void) {
struct pollfd fds[2];
int ret;
/* watch stdin for input */
fds[0].fd = STDIN_FILENO;
fds[0].events = POLLIN;
/* watch stdout for ability to write (almost always true) */
fds[1].fd = STDOUT_FILENO;
fds[1].events = POLLOUT;
/* All set, block! */
ret = poll (fds, 2, TIMEOUT * 1000);
if (ret == −1) {
perror ("poll");
return 1;
}
if (!ret) {
printf ("%d seconds elapsed.\n", TIMEOUT);
return 0;
}
if (fds[0].revents & POLLIN)
printf ("stdin is readable\n");
if (fds[1].revents & POLLOUT)
printf ("stdout is writable\n");
return 0;
}
poll vs select
poll基于select进行改进:
poll不需要用户计算 fd 集合数量的最大值;poll对应处理 fd 的索引值较大的情况时,效率更高。具体来说,在select中,如果仅仅检测一个值为900的 fd 时,内核需要从0开始扫描各个 fd ,直到第900个(因为在调用select时,需要传入值最大的 fd 的数字);而在poll中,只需要传入一个长度为1的pollfd数组,从而避免了从1-900的 fd 扫描;- 开发者在调用
poll时,更加方便。在select中, fd 集合会在select调用返回时重新构造,因此在下一次调用select时,必须重新构造 fd 集合;而在poll中,由于events域和revents域分离,在下一次调用poll时,开发者不需要再重新构造 fd 集合。