NAT

SNAT (Source NAT) and DNAT (Destination NAT)
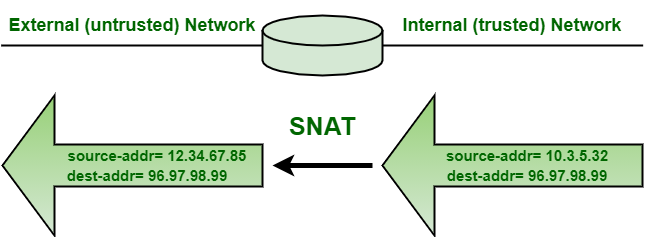
SNAT, as name suggests, is a technique that translates source IP address generally when connecting from private IP address to public IP address. It maps source client IP address in a request to a translation defined on BIG-IP device. It is most common form of NAT that is used when internal host needs to initiate session to an external host or public host.
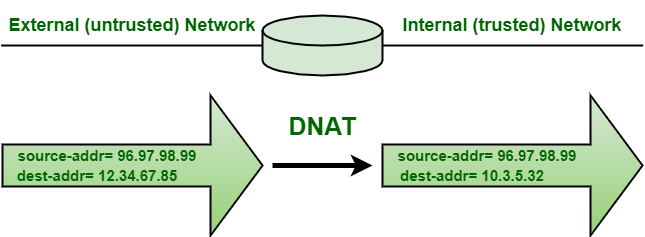
DNAT, as name suggests, is a technique that translates destination IP address generally when connecting from public IP address to private IP address. It is generally used to redirect packets destined for specific IP address or specific port on IP address, on one host simply to a different address mostly on different host.
Reference
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Network_address_translation
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/load-balancer/load-balancer-outbound-connections
- https://techdocs.f5.com/kb/en-us/products/big-ip_ltm/manuals/product/tmos-routing-administration-11-6-0/7.html
FEATURED TAGS
algorithm
algorithmproblem
architecturalpattern
architecture
aws
blockchain
c#
cachesystem
codis
compile
concurrentcontrol
database
dataformat
datastructure
debug
design
designpattern
distributedsystem
django
docker
domain
engineering
freebsd
git
golang
grafana
hackintosh
hadoop
hardware
hexo
http
hugo
ios
iot
java
javaee
javascript
kafka
kubernetes
linux
linuxcommand
linuxio
lock
macos
markdown
microservices
mysql
nas
network
networkprogramming
nginx
node.js
npm
oop
openwrt
operatingsystem
padavan
performance
programming
prometheus
protobuf
python
redis
router
security
shell
software testing
spring
sql
systemdesign
truenas
ubuntu
vmware
vpn
windows
wmware
wordpress
xml
zookeeper