Proxy
正向代理 Forward Proxy (Proxy Server)
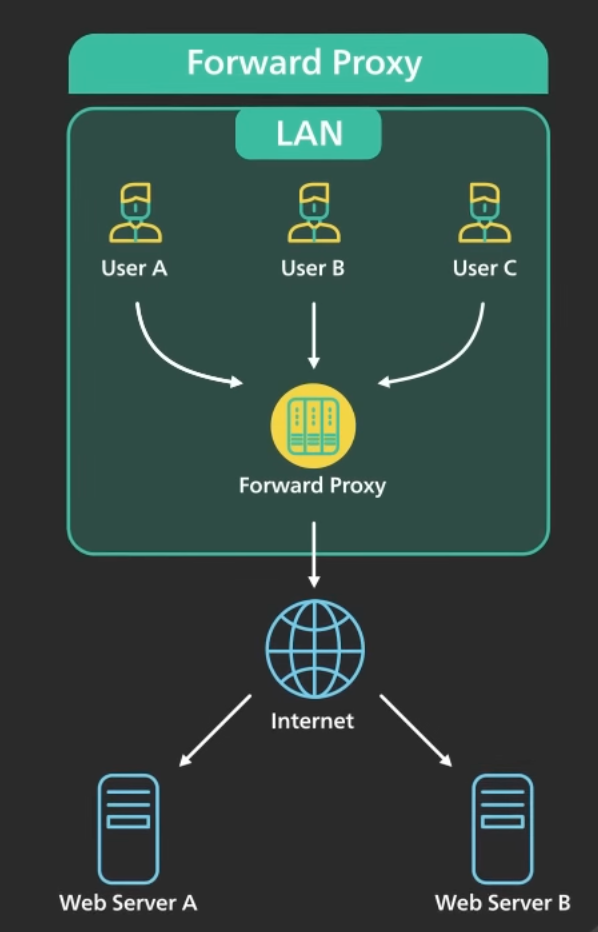
In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource
Instead of connecting directly to a server that can fulfill a request for a resource, such as a file or web page, the client directs the request to the proxy server, which evaluates the request and performs the required network transactions. This serves as a method to simplify or control the complexity of the request, or provide additional benefits such as load balancing, privacy, or security. Proxies were devised to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems. A proxy server thus functions on behalf of the client when requesting service, potentially masking the true origin of the request to the resource server.
反向代理(Reverse Proxy)
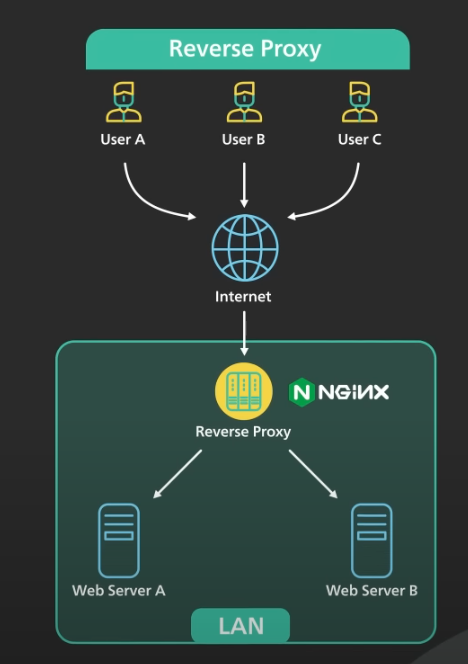
In computer networks, a reverse proxy is an application that sits in front of back-end applications and forwards client (e.g. browser) requests to those applications. Reverse proxies help increase scalability, performance, resilience and security. The resources returned to the client appear as if they originated from the web server itself.
Large websites and content delivery networks use reverse proxies, together with other techniques, to balance the load between internal servers. Reverse proxies can keep a cache of static content, which further reduces the load on these internal servers and the internal network. It is also common for reverse proxies to add features such as compression or TLS encryption to the communication channel between the client and the reverse proxy.
Reverse proxies are typically owned or managed by the web service, and they are accessed by clients from the public Internet. In contrast, a forward proxy is typically managed by a client (or their company) who is restricted to a private, internal network, except that the client can ask the forward proxy to retrieve resources from the public Internet on behalf of the client.
反向代理(reverse proxy),是指以代理服务器来接受internet上的连接请求,然后将请求转发给内部网络上的服务器,并将从服务器上得到的结果返回给internet上请求连接的客户端,此时代理服务器对外就表现为一个反向代理服务器。
反向代理的作用就比较多了,这里简单列举一下:
- 保护和隐藏原始资源服务器
- 加密和SSL加速
- 负载均衡
- 缓存静态内容
- 压缩
- 减速上传
- 安全
- 外网发布
Protocols
SOCKS
Proxy Solutions
microsocks
https://github.com/rofl0r/microsocks
$ git clone https://github.com/rofl0r/microsocks.git; cd microsocks; sudo make install
$ which microsocks
/usr/local/bin/microsocks
$ microsocks
Verify
# connect to https://ifconfig.co via 127.0.0.1:1080
$ curl https://ifconfig.co --socks5 127.0.0.1:1080 [--proxy-user sockd:sockd]
Start on boot
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/microsocks.service
[Unit]
Description=Microsocks Service
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/microsocks -p 1080 # 替换 1080 为你想要的端口号
User=nobody # 或者其他你希望运行此服务的用户
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
sudo systemctl daemon-reload; sudo systemctl enable microsocks; sudo systemctl start microsocks
sudo systemctl status microsocks
Dante
https://github.com/Lozy/danted
3proxy
https://github.com/3proxy/3proxy
$ sudo systemctl stop 3proxy.service
Reference
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOCKS
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reverse_proxy
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_server
- https://www.imperva.com/learn/performance/reverse-proxy/