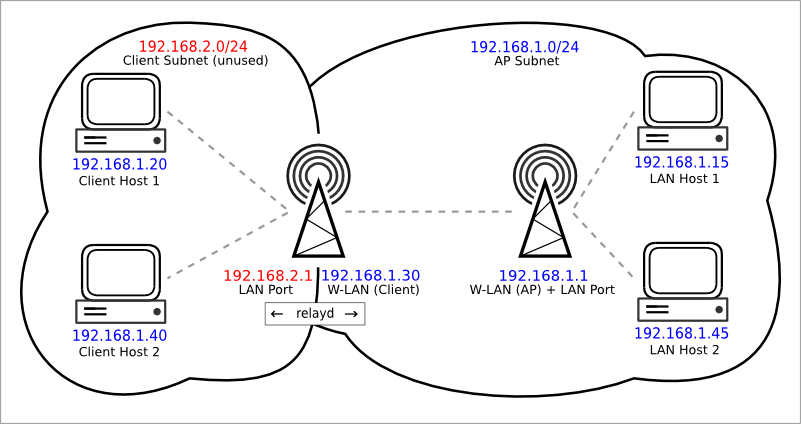
This image shows an example setup. LAN interface of the Wi-Fi extender device MUST be on a different subnet for relayd to work (since it is routing traffic, it expects 2 different subnets).
Since both ethernet ports and Access Point Wi-Fi network are on the same LAN interface, all clients connecting to the Ethernet ports and to the Access Point Wi-Fi network of the Wi-Fi extender device will be routed by relayd and will be connected to your main network.
The LAN interface subnet will be used only as a “management” interface, as devices connecting to the Wi-Fi repeater will be on the main network’s subnet instead. You will have to set your PC with a static address in the same subnet as the LAN interface (like 192.168.2.10 for our example) to connect again to the Wi-Fi repeater’s Luci GUI or SSH.
...