Leader-based Replication (Active/passive or Master–slave Replication)
Each node that stores a copy of the database is called a replica.
Every write to the database needs to be processed by every replica; otherwise, the replicas would no longer contain the same data. The most common solution for this is called leader-based replication (also known as active/passive or master–slave replication)
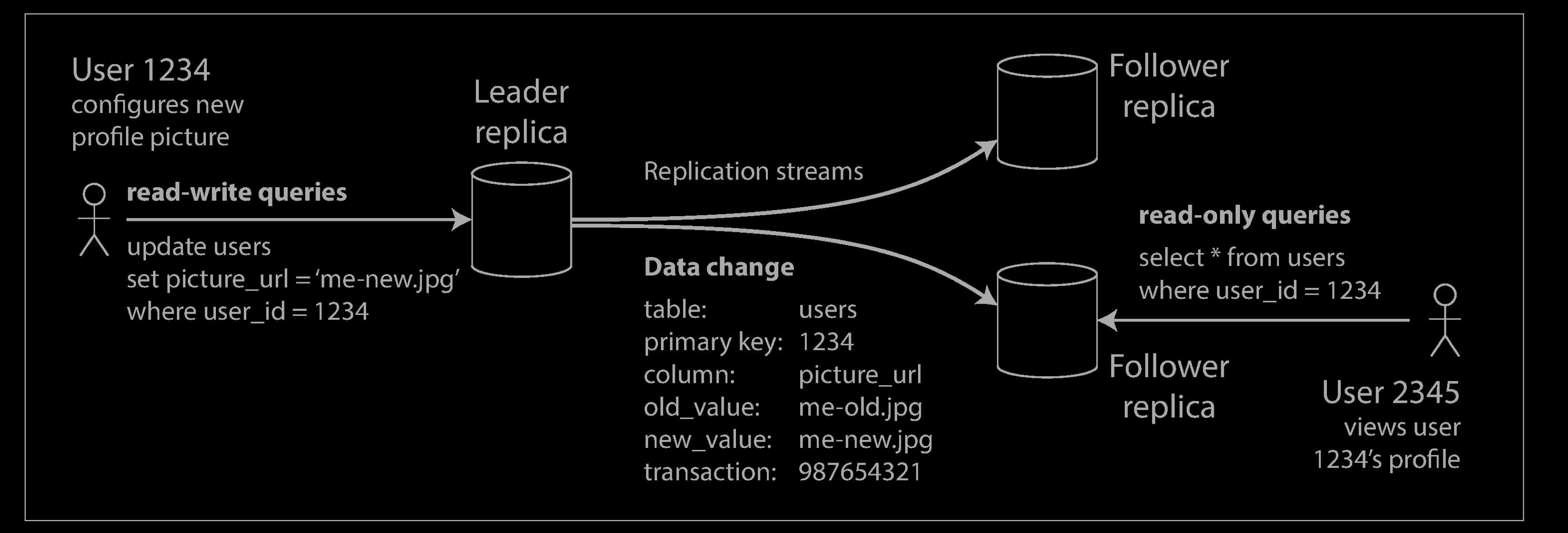
- One of the replicas is designated the leader (also known as master or primary). When clients want to write to the database, they must send their requests to the leader, which first writes the new data to its local storage.
- The other replicas are known as followers (read replicas, slaves, secondaries, or hot standbys). Whenever the leader writes new data to its local storage, it also sends the data change to all of its followers as part of a replication log or change stream. Each follower takes the log from the leader and updates its local copy of the database accordingly, by applying all writes in the same order as they were processed on the leader.
- When a client wants to read from the database, it can query either the leader or any of the followers. However, writes are only accepted on the leader (the followers are read-only from the client’s point of view).
