select
select是基于I/O多路复用模型。select 可以让内核在"多个 fd 对应的I/O操作中任何一个“就绪"(指数据已经被拷贝到kernel space)或"经过指定时间后",唤醒(wake)并通知用户线程(在唤醒之前,用户线程因为被阻塞而处于sleep状态)。比如:
- 当1、4或5中任何一个 fd 的状态为可读时
- 或当4、7中任何一个 fd 的状态为可写时
- 或当6、8中任何一个 fd 的处理过程中抛出异常时
- 或经过10.2秒后
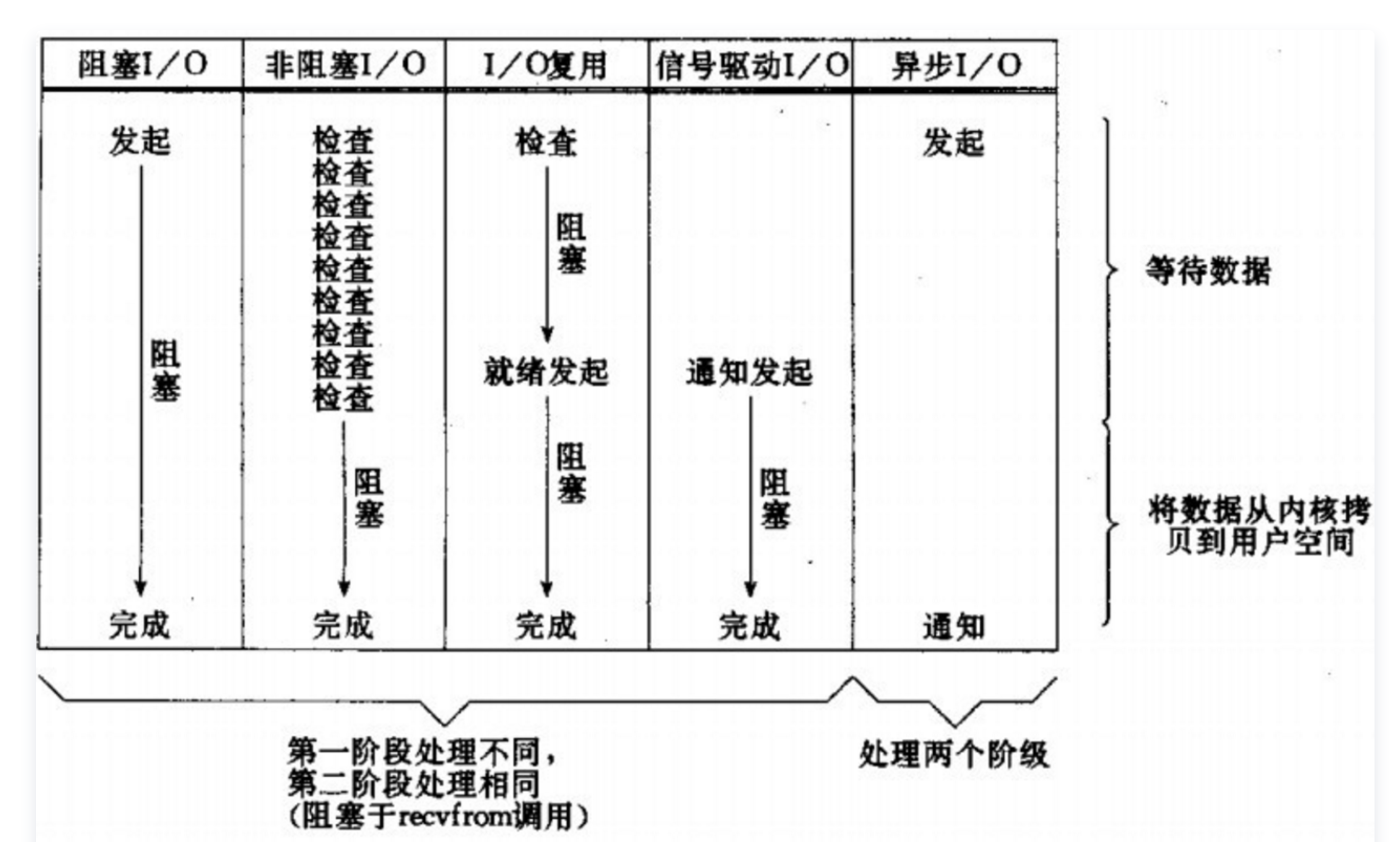
由于在select和poll中,每一次检查监听的 fd 状态变化时,都需要遍历一次用户传入的 fd 集合,因而如果当 fd 的数量很多时,一次集合遍历将会非常耗时。
为了解决这个问题,在select和poll的基础上进行优化,在Linux kernel 2.6中,引入了event poll(epoll)方法。
epoll将 fd 的监测声明和真正的监测进行了分离。
从实现的角度来说,epoll会创建一个epoll instance ,这个epoll instance 对应一个 fd 。同时,这个epoll instance 中包含一个 fd 集合(称为epoll set或interest list),集合中存储了所有希望被监听的 fd 。当某个 fd 对应的I/O操作完成时,这个 fd 会被放入ready list,ready list是epoll set的子集。
该方案是Linux下效率最高的I/O事件通知机制。本质在于epoll基于内核层面的事件通知。具体来说,epoll不是在用户线程发起轮询调用后,不断地去检查所有监听的 fd 是否状态发生变化(poll和select是这样做的),而是在当这些 fd 中任何一个发生状态变化时,内核就将这些对应的 fd 移动到epoll实例中的ready list中(这里发生了一次内核事件通知)。因此,当用户线程调用轮询方法epoll_wait时,内核不再需要进行一次 fd 的状态变化检查的遍历,而是直接返回结果。
下图为通过epoll方式实现轮询的示意图:
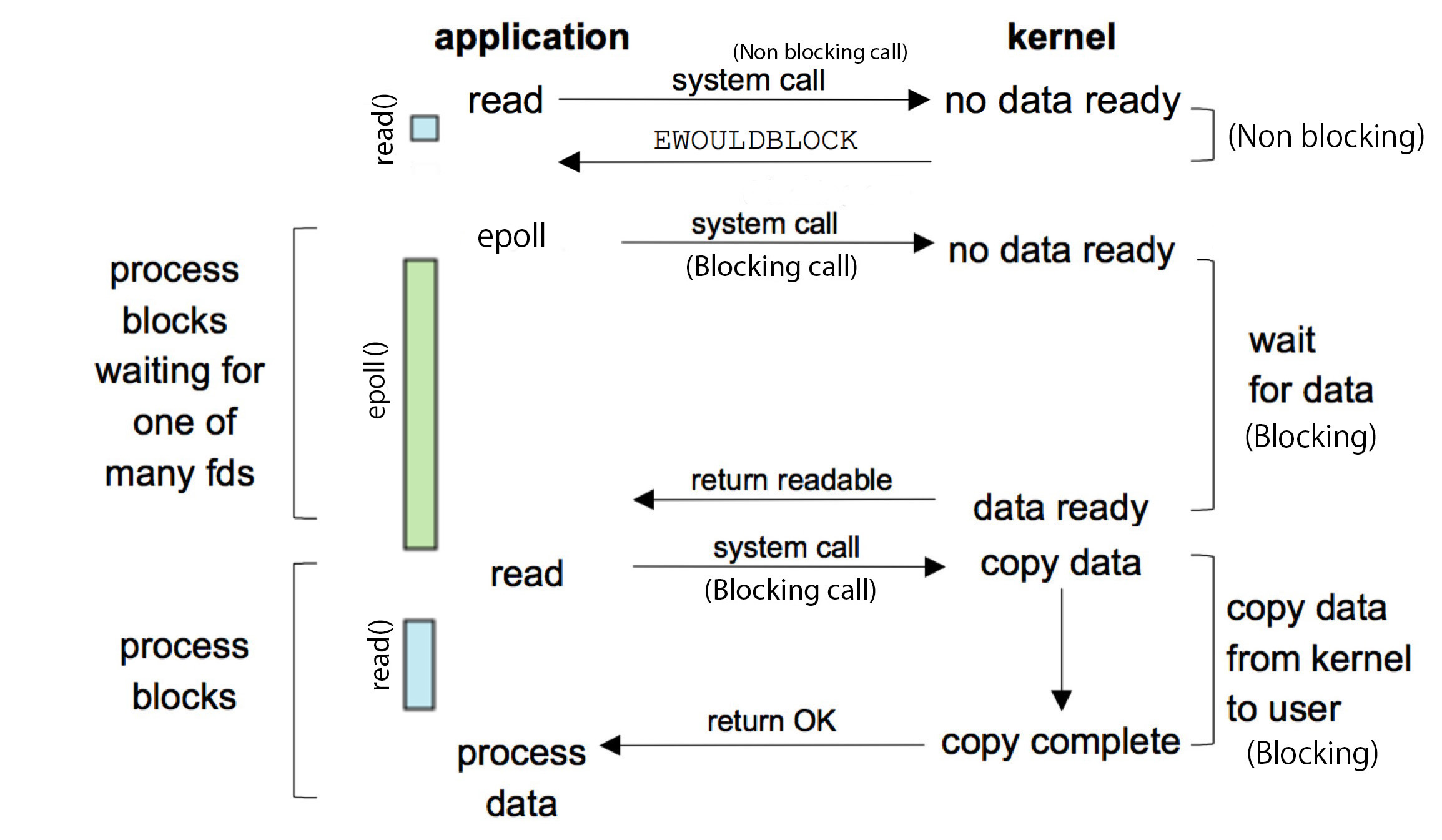
epollepoll stands for event poll and is a Linux kernel system call for a scalable I/O event notification mechanism, first introduced in version 2.5.44 of the Linux kernel.
Its function is to monitor multiple file descriptors to see whether I/O is possible on any of them. It is meant to replace the older POSIX select(2) and poll(2) system calls, to achieve better performance in more demanding applications, where the number of watched file descriptors is large (unlike the older system calls, which operate in O(n) time, epoll operates in O(1) time.
Reflection is just a mechanism to examine the type and value pair stored inside an interface variable. To get started, there are two types we need to know about in package reflect: Type and Value. Those two types give access to the contents of an interface variable, and two simple functions, called reflect.TypeOf and reflect.ValueOf, retrieve reflect.Type and reflect.Value pieces out of an interface value.